Energy-Efficient Appliance Buying Guide 2025: Save Money and Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
In today’s environmentally conscious world, choosing energy-efficient appliances isn’t just good for the planet—it’s also great for your wallet. The average American household spends over $2,000 annually on energy bills, with appliances accounting for a significant portion of this cost. By making smart choices when purchasing new appliances, you can reduce your energy consumption by 10-50% depending on the appliance type and usage patterns.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about getting energy-efficient appliances that meet your needs while also minimizing environmental impact and long-term costs.
Understanding Energy Efficiency Labels and Ratings in Appliance
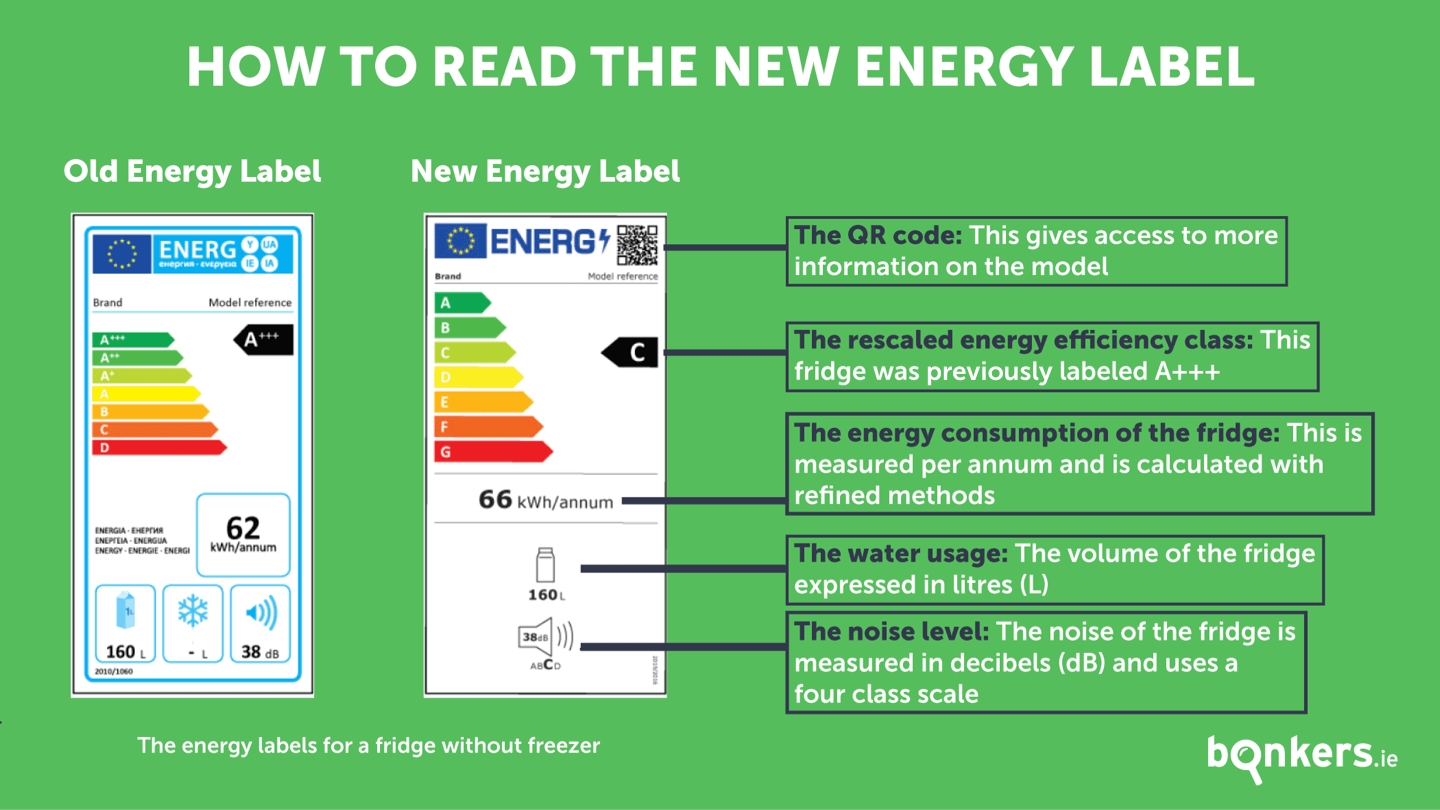
What Do Energy Star Ratings Really Mean?
When shopping for appliances, you’ll encounter various energy efficiency labels, with Energy Star being the most recognized in the United States. An Energy Star certification indicates that the appliance meets strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Energy Star appliances typically use 10-50% less energy than standard models, translating to significant savings over the appliance’s lifetime. For example, an Energy Star certified refrigerator uses about 9% less energy than models that meet the federal minimum standard.
Get your Appliances; Here
Decoding EnergyGuide Labels
The yellow EnergyGuide label provides valuable information about an appliance’s energy consumption. These labels display:
- Estimated annual operating cost
- Estimated yearly electricity consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh)
- Energy efficiency rating compared to similar models
Pay special attention to the estimated annual operating cost when comparing different models—this figure helps you understand the long-term financial impact of your purchase.
Calculating the True Cost of Appliances
Purchase Price vs. Lifetime Cost
When budgeting for a new appliance, many consumers focus solely on the purchase price. However, the true cost of an appliance includes:
- Initial purchase price
- Installation costs
- Annual energy costs
- Maintenance expenses
- Expected lifespan
A higher-priced, energy-efficient model often costs less in the long run than a cheaper, less efficient alternative. Use this simple formula to calculate the lifetime cost:
Lifetime Cost = Purchase Price + (Annual Energy Cost × Expected Lifespan) + Estimated Maintenance Costs
Return on Investment (ROI) for Energy-Efficient Appliances
Energy-efficient appliances typically have a higher upfront cost but lower operating expenses. To determine if the premium is worth it, calculate the payback period:
Payback Period = (Price Difference) ÷ (Annual Energy Savings)
For example, if an energy-efficient refrigerator costs $200 more but saves $50 annually on electricity, the payback period would be 4 years. Considering most refrigerators last 10-15 years, this represents a good investment.
Choosing Energy-Efficient Refrigerators
Key Features to Look For
Refrigerators are among the biggest energy consumers in your home since they run continuously. When shopping for an energy-efficient refrigerator, consider:
- Configuration: Side-by-side models typically use more energy than top-freezer designs. According to the Department of Energy, top-freezer models use approximately 10-25% less energy than side-by-side or bottom-freezer models.
- Size: Choose appropriately sized refrigerators—larger models consume more energy. The most efficient size for most households is between 16-20 cubic feet.
- Features: Auto-defrost, ice makers, and water dispensers increase energy consumption. Consider whether these conveniences are worth the additional energy cost.
Optimal Temperature Settings
Set your refrigerator temperature between 35-38°F (1.7-3.3°C) and your freezer at 0°F (-18°C) for optimal energy efficiency without compromising food safety.
Energy-Efficient Washing Machines and Dryers
Front-Load vs. Top-Load Washers
Front-loading washing machines typically use 25% less energy and 33% less water than traditional top-loading models. They extract more water during the spin cycle, reducing drying time and energy consumption.
High-efficiency (HE) washers feature:
- Lower water usage (20-66% less than traditional models)
- Faster spin speeds, reducing drying time
- Specialized detergent requirements to prevent excess suds
Heat Pump Dryers: The Future of Efficient Drying
Heat pump dryers represent the cutting edge in energy-efficient laundry technology, using 20-60% less energy than conventional models. These dryers:
- Recycle hot air rather than venting it outside
- Operate at lower temperatures, being gentler on clothes
- Often don’t require external venting, offering more installation flexibility
While they come with a higher price tag, heat pump dryers can save substantial energy over their lifetime, especially in households that dry multiple loads weekly.
Smart Appliances and Energy Management
Do Smart Features Actually Save Energy?
Smart appliances connect to your home network, allowing remote monitoring and control. While not inherently more energy-efficient, they can help reduce consumption through:
- Optimal cycle selection: Smart washers can recommend the most efficient cycle based on load size and soil level.
- Peak hour avoidance: Smart appliances can be programmed to run during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower.
- Usage analytics: Many smart appliances provide detailed energy consumption data, helping you identify opportunities for greater efficiency.
Integrating with Home Energy Management Systems
For maximum efficiency, consider integrating smart appliances with a home energy management system. These systems can automatically optimize energy usage based on:
- Time-of-use electricity pricing
- Solar panel production (if applicable)
- Occupancy patterns
- Weather conditions
Dishwashers: Efficiency Beyond Energy
Water Usage Considerations
Energy-efficient dishwashers not only save electricity but also conserve water. Modern efficient models use as little as 3 gallons per cycle, compared to 10-15 gallons for hand washing the same dishes.
Key features to look for include:
- Soil sensors: These adjust the cycle length and water usage based on how dirty your dishes are.
- Multiple wash arms: These improve cleaning efficiency while potentially using less water.
- Filtration systems: Good filtration means less water is needed for rinsing.
Best Practices for Efficient Dishwasher Use
To maximize efficiency:
- Run full loads only
- Skip the pre-rinse (most modern dishwashers don’t require it)
- Use the eco or light wash cycle for regularly soiled dishes
- Allow dishes to air dry instead of using the heat dry option
HVAC Systems: The Biggest Energy Users
Understanding SEER, EER, and HSPF Ratings
When shopping for heating and cooling systems, you’ll encounter several efficiency ratings:
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): For air conditioners and heat pumps in cooling mode. Higher numbers indicate better efficiency, with modern efficient units rating 16 or higher.
- EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio): Similar to SEER but measured at peak conditions. Look for ratings of 12 or higher.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): For heat pumps in heating mode. Efficient models have ratings of 8.5 or higher.
According to the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, upgrading from a SEER 10 to SEER 16 air conditioner can reduce cooling energy consumption by about 38%.
Matching Systems to Your Climate
The most efficient HVAC solution depends on your local climate:
- Hot, humid climates: Focus on high SEER air conditioners with good humidity control.
- Mixed climates: Consider dual-fuel systems combining heat pumps with gas furnaces.
- Cold climates: Look for heat pumps specifically designed for cold weather or high-efficiency furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Investing in energy-efficient appliances is a win-win scenario—reducing both environmental impact and long-term household expenses. When shopping for new appliances:
- Always check for Energy Star certification
- Compare EnergyGuide labels between similar models
- Calculate lifetime costs rather than focusing solely on purchase price
- Consider your specific usage patterns and household needs
- Look beyond energy to other resource considerations like water usage
By making informed choices about energy-efficient appliances, you can reduce your household energy consumption by 10-50% while enjoying modern conveniences and potentially increasing your home’s value.
Remember that even the most efficient appliances should be properly maintained to ensure optimal performance throughout their lifespan. Regular maintenance not only preserves efficiency but also extends the life of your investment.








